分布式锁
概述
分布式锁指的是,所有服务中的所有线程都去获取同一把锁,但只有一个线程可以成功的获得锁,其他没有获得锁的线程必须全部等待,直到持有锁的线程释放锁。
分布式锁是可以跨越多个实例,多个进程的锁

分布式锁具备的条件:
- 互斥性:任意时刻,只能有一个客户端持有锁
- 锁超时释放:持有锁超时,可以释放,防止死锁
- 可重入性:一个线程获取了锁之后,可以再次对其请求加锁
- 高可用、高性能:加锁和解锁开销要尽可能低,同时保证高可用
- 安全性:锁只能被持有该锁的服务(或应用)释放。
- 容错性:在持有锁的服务崩溃时,锁仍能得到释放,避免死锁。
分布式锁实现方案
分布式锁都是通过第三方组件来实现的,目前比较流行的分布式锁的解决方案有:
- 数据库,通过数据库可以实现分布式锁,但是在高并发的情况下对数据库压力较大,所以很少使用。
- Redis,借助Redis也可以实现分布式锁,而且Redis的Java客户端种类很多,使用的方法也不尽相同。
- Zookeeper,Zookeeper也可以实现分布式锁,同样Zookeeper也存在多个Java客户端,使用方法也不相同
Redis实现分布式锁
SETNX
基本方案:Redis提供了setXX指令来实现分布式锁
格式: setnx key value
将key 的值设为value ,当且仅当key不存在。
若给定的 key已经存在,则SETNX不做任何动作。
设置分布式锁后,能保证并发安全,但上述代码还存在问题,如果执行过程中出现异常,程序就直接抛出异常退出,导致锁没有释放造成最终死锁的问题。(即使将锁放在finally中释放,但是假如是执行到中途系统宕机,锁还是没有被成功的释放掉,依然会出现死锁现象)
设置超时时间
SET lock_key unique_value NX PX 10000但是,即使设置了超时时间后,还存在问题。
假设有多个线程,假设设置锁的过期时间10s,线程1上锁后执行业务逻辑的时长超过十秒,锁到期释放锁,线程2就可以获得锁执行,此时线程1执行完删除锁,删除的就是线程2持有的锁,线程3又可以获取锁,线程2执行完删除锁,删除的是线程3的锁,如此往后,这样就会出问题。
让线程只删除自己的锁
解决办法就是让线程只能删除自己的锁,即给每个线程上的锁添加唯一标识(这里UUID实现,基本不会出现重复),删除锁时判断这个标识:
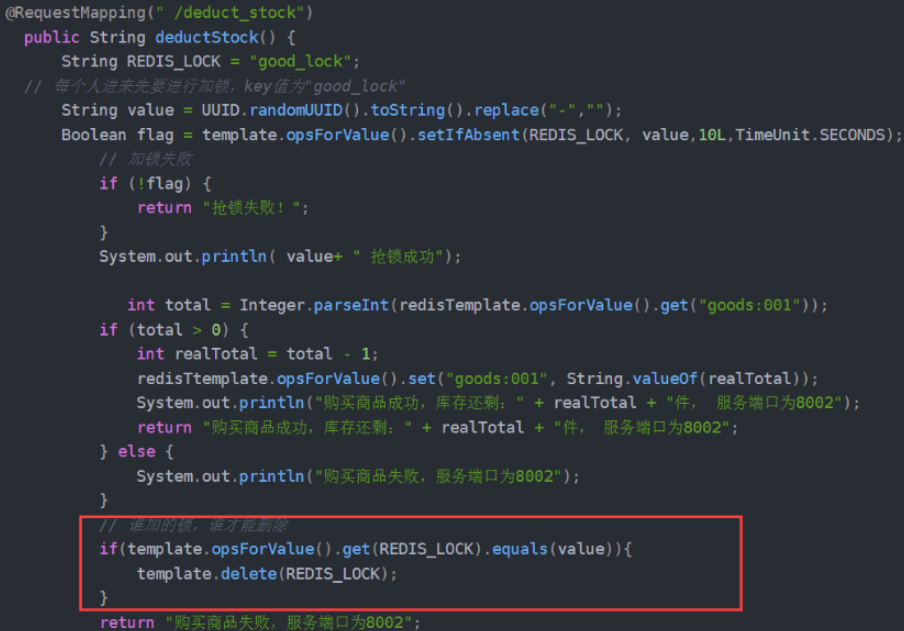
但上述红框中由于判定和释放锁不是原子的,极端情况下,可能判定可以释放锁,在执行删除锁操作前刚好时间到了,其他线程获取锁执行,前者线程删除锁删除的依然是别的线程的锁,所以要让删除锁具有原子性,可以利用redis事务或lua脚本实现原子操作判断+删除
Redis的单条命令操作是原子性的,但是多条命令操作并不是原子性的,因此Lua脚本实现的就是令Redis的多条命令也实现原子操作
redis事务不是原子操作的,详情请看 Redis的事务
但是,可以利用Redis的事务和watch实现的乐观锁 来监视锁的状态
@RequestMapping(" /deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
String REDIS_LOCK = "good_lock";
// 每个人进来先要进行加锁,key值为"good_lock"
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-","");
try{
// 为key加一个过期时间
Boolean flag = template.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(REDIS_LOCK, value,10L,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 加锁失败
if(!flag){
return "抢锁失败!";
}
System.out.println( value+ " 抢锁成功");
String result = template.opsForValue().get("goods:001");
int total = result == null ? 0 : Integer.parseInt(result);
if (total > 0) {
// 如果在此处需要调用其他微服务,处理时间较长。。。
int realTotal = total - 1;
template.opsForValue().set("goods:001", String.valueOf(realTotal));
System.out.println("购买商品成功,库存还剩:" + realTotal + "件, 服务端口为8002");
return "购买商品成功,库存还剩:" + realTotal + "件, 服务端口为8002";
} else {
System.out.println("购买商品失败,服务端口为8002");
}
return "购买商品失败,服务端口为8002";
}finally {
// 谁加的锁,谁才能删除
// 也可以使用redis事务
// https://redis.io/commands/set
// 使用Lua脚本,进行锁的删除
Jedis jedis = null;
try{
jedis = RedisUtils.getJedis();
String script = "if redis.call('get',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] " +
"then " +
"return redis.call('del',KEYS[1]) " +
"else " +
" return 0 " +
"end";
Object eval = jedis.eval(script, Collections.singletonList(REDIS_LOCK), Collections.singletonList(value));
if("1".equals(eval.toString())){
System.out.println("-----del redis lock ok....");
}else{
System.out.println("-----del redis lock error ....");
}
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
if(null != jedis){
jedis.close();
}
}
// redis事务
// while(true){
// template.watch(REDIS_LOCK);
// if(template.opsForValue().get(REDIS_LOCK).equalsIgnoreCase(value)){
// template.setEnableTransactionSupport(true);
// template.multi();
// template.delete(REDIS_LOCK);
// List<Object> list = template.exec();
// if(list == null){
// continue;
// }
// }
// template.unwatch();
// break;
// }
}
}
}尽管这样,还是会有问题,锁超时释放虽然可以避免死锁,但如果是业务执行耗时较长,也会导致锁的释放,但其实此时业务还在执行中,还是应该将业务执行结束之后再释放锁。
续时
因此可以设定,任务不完成,锁就不释放。
可以维护一个定时线程池 ScheduledExecutorService,每隔 2s 去扫描加入队列中的 Task,判断失效时间是否快到了,如果快到了,则给锁续上时间。
那如何判断是否快到失效时间了呢?可以用以下公式:【失效时间】<= 【当前时间】+【失效间隔(三分之一超时)】
// 扫描的任务队列
private static ConcurrentLinkedQueue<RedisLockDefinitionHolder> holderList = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
/**
* 线程池,维护keyAliveTime
*/
private static final ScheduledExecutorService SCHEDULER = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1,
new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("redisLock-schedule-pool").daemon(true).build());
{
// 两秒执行一次「续时」操作
SCHEDULER.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
// 这里记得加 try-catch,否者报错后定时任务将不会再执行=-=
Iterator<RedisLockDefinitionHolder> iterator = holderList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
RedisLockDefinitionHolder holder = iterator.next();
// 判空
if (holder == null) {
iterator.remove();
continue;
}
// 判断 key 是否还有效,无效的话进行移除
if (redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(holder.getBusinessKey()) == null) {
iterator.remove();
continue;
}
// 超时重试次数,超过时给线程设定中断
if (holder.getCurrentCount() > holder.getTryCount()) {
holder.getCurrentTread().interrupt();
iterator.remove();
continue;
}
// 判断是否进入最后三分之一时间
long curTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean shouldExtend = (holder.getLastModifyTime() + holder.getModifyPeriod()) <= curTime;
if (shouldExtend) {
holder.setLastModifyTime(curTime);
redisTemplate.expire(holder.getBusinessKey(), holder.getLockTime(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.info("businessKey : [" + holder.getBusinessKey() + "], try count : " + holder.getCurrentCount());
holder.setCurrentCount(holder.getCurrentCount() + 1);
}
}
}, 0, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}Redisson
使用Redis + lua方式可能存在的问题
- 不可重入性。同一个线程无法多次获取同一把锁
- 不可重试。获取锁只尝试一次就返回false,没有重试机制
- 超时释放。锁超时释放虽然可以避免死锁,但如果是业务执行耗时较长,也会导致锁的释放,存在安全隐患
- 主从一致性。如果Redis是主从集群,主从同步存在延迟,当主机宕机时,从成为了主,但可能存在从此时还未完成同步,因此从上就没有锁标识,此时会出现线程安全问题。
RLock是Redisson分布式锁的最核心接口,继承了concurrent包的Lock接口和自己的RLockAsync接口,RLockAsync的返回值都是RFuture,是Redisson执行异步实现的核心逻辑,也是Netty发挥的主要阵地。
RLock如何加锁解锁,实现可重入性?
从RLock进入,找到RedissonLock类,找到tryLock 方法再继续找到tryAcquireOnceAsync 方法,这是加锁的主要代码(版本不一此处实现有差别,和最新3.15.x有一定出入,但是核心逻辑依然未变。此处以3.13.6为例)
// waitTime 等待时间,多久时间内都会在这尝试获取锁
// leaseTime 加锁时是否设置过期时间
private RFuture<Boolean> tryAcquireOnceAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
} else {
RFuture<Boolean> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
if (ttlRemaining) {
this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}此处出现leaseTime时间判断的2个分支,实际上就是加锁时是否设置过期时间,未设置过期时间(-1)时则会有watchDog 的锁续约 (下文),一个注册了加锁事件的续约任务。我们先来看有过期时间tryLockInnerAsync 部分
evalWriteAsync方法是eval命令执行lua的入口
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command, "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId));
}eval命令执行Lua脚本的地方,此处将Lua脚本展开
-- 不存在该key时
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then
-- 新增该锁并且hash中该线程id对应的count置1
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
-- 设置过期时间
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
-- 存在该key 并且 hash中线程id的key也存在
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then
-- 线程重入次数++
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);// keyName
KEYS[1] = Collections.singletonList(this.getName())
// leaseTime
ARGV[1] = this.internalLockLeaseTime
// uuid+threadId组合的唯一值
ARGV[2] = this.getLockName(threadId)总共3个参数完成了一段逻辑:
- 判断该锁是否已经有对应hash表存在,
- 没有对应的hash表:则set该hash表中一个entry的key为锁名称,value为1,之后设置该hash表失效时间为leaseTime
- 存在对应的hash表:则将该lockName的value执行+1操作,也就是计算进入次数,再设置失效时间leaseTime
- 最后返回这把锁的ttl剩余时间
再看看RLock如何解锁?
看unlock方法,同样查找方法名,一路到unlockInnerAsync
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN, "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then return nil;end; local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); if (counter > 0) then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); return 0; else redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); return 1; end; return nil;", Arrays.asList(this.getName(), this.getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId));
}将lua脚本展开
-- 不存在key
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then
return nil;
end;
-- 存在,计数器 -1
local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1);
if (counter > 0) then
-- 过期时间重设
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]);
return 0;
else
-- 删除并发布解锁消息
redis.call('del', KEYS[1]);
redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]);
return 1;
end;
return nil;该Lua KEYS有2个Arrays.asList(getName(), getChannelName())
name 锁名称
channelName,用于pubSub发布消息的channel名称ARGV变量有三个LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId)
LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE,channel发送消息的类别,此处解锁为0
internalLockLeaseTime,watchDog配置的超时时间,默认为30s
lockName 这里的lockName指的是uuid和threadId组合的唯一值具体执行步骤如下:
- 如果该锁不存在则返回nil;
- 如果该锁存在则将其线程的hash key计数器-1,
- 计数器counter>0,重置下失效时间,返回0;否则,删除该锁,发布解锁消息unlockMessage,返回1;
加锁解锁流程总结如下:
总的来说就是通过Hash类型来存储锁的次数:
RLock的锁重试问题
需要分析的是锁重试的,所以,在使用lock.tryLock()方法的时候,不能用无参的。
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return this.tryLock(waitTime, -1L, unit);
}在调用tryAcquire方法后,返回了一个Long的ttl
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
} else {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
} else {
//省略继续跟着代码进去查看,最后会发现,调用tryLockInnerAsync方法。这个方法就是获取锁的Lua脚本的。
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command, "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId));
}这个lua脚本上面提到了。就是 判断,如果获取到锁,返回一个nil.也就是null。如果没有获取到,就调用 pttl,name。其实就是获取当前name锁的剩余有效期。
获取到ttl。如果返回null说获取锁成功,直接返回true.如果返回的不是null,说明需要进行重试操作了。主要是根据时间进行判断的。经过一系列判断后,do,while是真正执行重试相关逻辑的。如下:
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
//如果返回null,说明获取到了锁,直接返回
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
} else {
//当前时间与进入方法时的时间进行比较
//System.currentTimeMillis() - current表示前面获取锁消耗时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;////time是重试锁的等待时间,
if (time <= 0L) {//剩余等待时间,如果剩余等待时间<=0,设置获取锁失败。
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
} else {
//再次获取当前时间
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
//刚刚尝试完获取锁失败,如果继续立即尝试一般是获取不到锁的,因此这里选择订阅的方式
//订阅当前锁,在unlock释放锁的时候有个:redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); 所以这里就订阅了
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = this.subscribe(threadId);
//进行等待RFuture的结果,等多久?等time的时间
if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
//time时间过完了还没有等到锁释放的通知
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
//如果等待超时,就取消订阅
this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
});
}
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
//返回获取锁失败
return false;
} else {//到这里表示在tme时间内获得了释放锁的通知
boolean var16;
try {
//检查之前订阅等待的消耗时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0L) {//当前的剩余等待时间
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
boolean var20 = false;
return var20;
}
//这里开始进行重试相关逻辑。主要就是当前时间和进入方法时候的时间进行比较
do {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//这里就是第一次重试
ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {//null表示获取锁失败
var16 = true;
return var16;
}
//再试一次
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0L && ttl < time) { //也不是一直试,等别人释放
((RedissonLockEntry)subscribeFuture.getNow()).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
((RedissonLockEntry)subscribeFuture.getNow()).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
} while(time > 0L);//时间还充足,继续等待
//时间到期了,还没获取到锁,返回失败
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
var16 = false;
} finally {
this.unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
return var16;
}
}
}
}主要是do while机制进行锁重试的,while会检查时间是否还充足会继续循环。当然这个循环不是直接while(true)的盲等机制,而是利用信号量和订阅的方式实现的,会等别人释放锁,再进行尝试,这种方式对cpu友好
Redisson的超时续约
跟随tryLock代码,在RedissonLock类中的tryAcquireOnceAsync方法中,会看到如下代码:
private RFuture<Boolean> tryAcquireOnceAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1L) {//设置了锁过期时间
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
} else {
//leaseTime = -1时,即没有设置了锁过期时间
RFuture<Boolean> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),//,默认30秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
//ttlRemainingFuture完成以后
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e == null) {//没有抛异常
if (ttlRemaining) {//获取锁成功
this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);//自动更新续期时间的任务调度
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}- 在使用trylock的时候,如果设置了锁过期时间,就不会执行续命相关逻辑了。
- 其中默认的watchdogTimeout时间是30秒。
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry entry = new RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry();
//获取一个entry,将entry放到map里,getEntryName()就是当前锁名称。
//放到map里,即一个锁对应一个entry
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry oldEntry = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {//表示重入的,第二次放
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {//表示第一次放
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
this.renewExpiration();//第一次放,进行续约
}
}看门狗机制:在获取锁成功以后,开启一个定时任务,每隔一段时间就会去重置锁的超时时间,以确保锁是在程序执行完unlock手动释放的,不会发生因为业务阻塞,key超时而自动释放的情况。
到期续约方法:
private void renewExpiration() {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ee = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName());
if (ee != null) { //Timeout定时任务,或者叫周期任务
Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ent = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)RedissonLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName());
if (ent != null) {
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId != null) {
//执行续命的操作
RFuture<Boolean> future = RedissonLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
RedissonLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonLock.this.getName() + " expiration", e);
} else {
if (res) {
RedissonLock.this.renewExpiration();//再次调用
}
}
});
}
}
}
//刷新周期, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, 默认释放时间是30秒,除以3就是每10秒更新一次
//续命时间为1/3的过期时间,设置续命单位是秒
},this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
}查看renewExpirationAsync方法源码,其调用了Lua脚本执行续命操作的。
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN, "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return 1; end; return 0;", Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId));
}pexpire重置锁的有效期。
总体逻辑如下:
- 开启一个任务,10秒钟后执行
- 开始的这个任务中重置有效期。假设设置的是默认30秒,则重置为30秒
- 更新后又重复步骤1、2
那么什么时候取消这个续约的任务呢?在释放锁unlock时
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise();
RFuture<Boolean> future = this.unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((opStatus, e) -> {
//取消这个任务
this.cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
if (e != null) {
result.tryFailure(e);
} else if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: " + this.id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
} else {
result.trySuccess((Object)null);
}
});
return result;
}multilock解决主从一致性问题
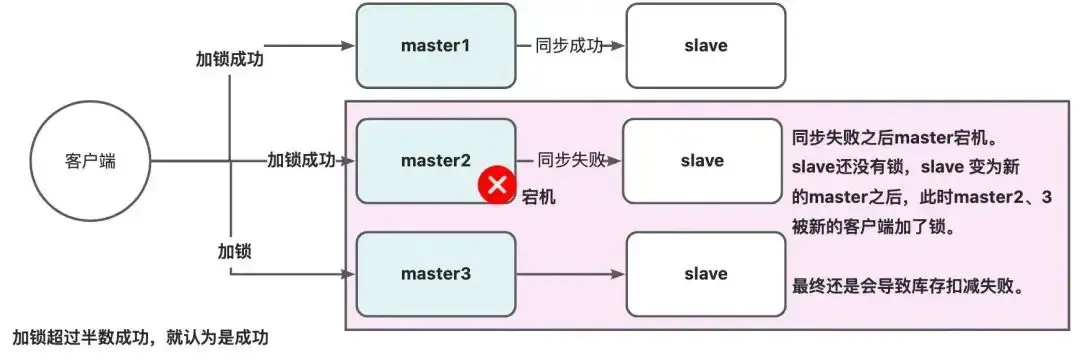
Redis分布式锁会有个缺陷,就是在Redis哨兵模式下:
- 客户端1对某个master节点写入了redisson锁,此时会异步复制给对应的slave节点。但是这个过程中一旦发生master节点宕机,主备切换,slave节点从变为了master节点。
- 客户端2来尝试加锁的时候,在新的master节点上也能加锁,此时就会导致多个客户端对同一个分布式锁完成了加锁。
- 系统在业务语义上一定会出现问题,导致各种脏数据的产生。
这个缺陷导致在哨兵模式或者主从模式下,如果master实例宕机的时候,可能导致多个客户端同时完成加锁。
因此redisson提出来了MutiLock锁,使用这把锁就不使用主从了,每个节点的地位都是一样的, 这把锁加锁的逻辑需要写入到每一个主丛节点上,只有所有的服务器都写入成功,此时才是加锁成功,假设现在某个节点挂了,那么他去获得锁的时候,只要有一个节点拿不到,都不能算是加锁成功,就保证了加锁的可靠性。
使用multilock()方法。必须在所有的节点都获取锁成功,才算成功。 缺点是运维成本高,实现复杂。
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Resource
private RedissonClient2 redissonClient2;
@Resource
private RedissonClient3 redissonClient3;
RLock lock = redissonClient.getMultilock(lock1,lock2,lock3)总结Redisson
Redisson分布式锁解决前三个问题原理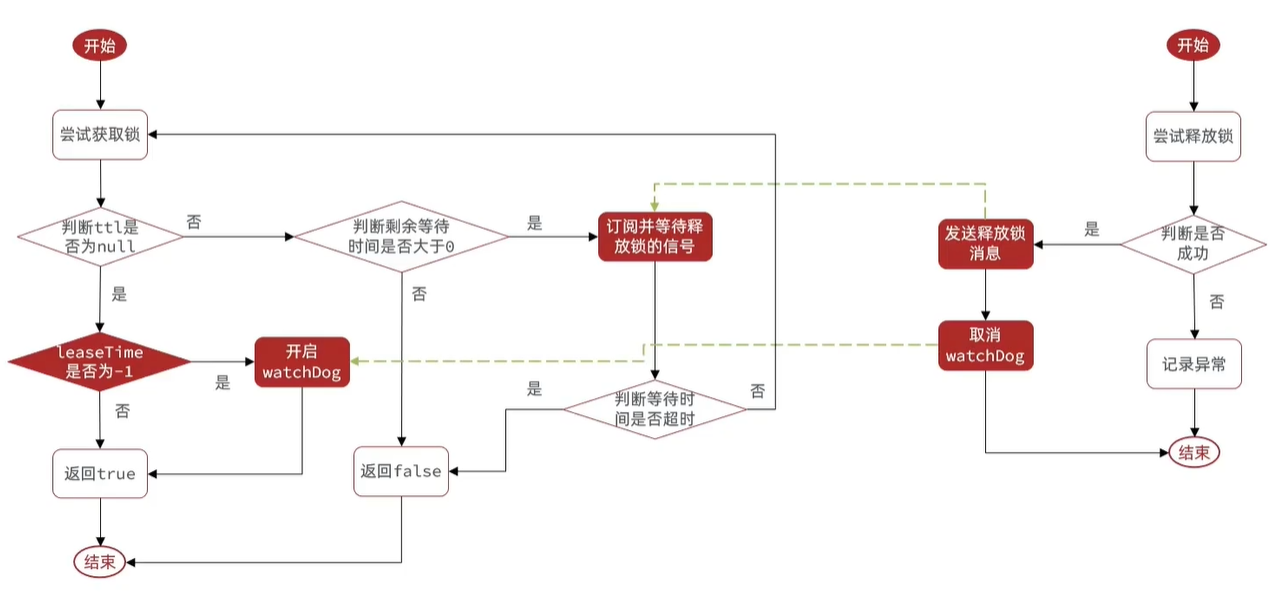
总结Redisson分布式锁原理:
- 可重入:利用hash结构记录线程id和重入次数
- 可重试:利用信号量和PubSub功能来实现等待、唤醒,获取锁失败的重试机制
- 超时续约:利用watchDog,开启一个定时任务,每隔一段时间(releaseTime/3),重置超时时间。
- 使用multilock: 多个独立的redis节点,必须在所有节点都获取重入锁,才算获取成功;
redLock
不管是redLock,还是redissonLock,两者底层都是通过相同的lua脚本来加锁、释放锁的,所以,两者只是外部形态的不同,底层是一样的。redLock是继承了redissonMultiLock,大部分的逻辑,都是在redissonMultiLock中去实现的,所以源码部分,大部分都是RedissonMultiLock
原理
- redLock的使用,需要有奇数台独立部署的Redis节点
- 在加锁的时候,会分别去N台节点上加锁,如果半数以上的节点加锁成功,就认为当前线程加锁成功