介绍
每个类都有一个 Class 对象,包含了与类有关的信息。当编译一个新类时,会产生一个同名的 .class 文件,该文件内容保存着 Class 对象。
类加载相当于 Class 对象的加载。类在第一次使用时才动态加载到 JVM 中,可以使用 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") 这种方式来控制类的加载,该方法会返回一个 Class 对象。
反射可以提供运行时的类信息,并且这个类可以在运行时才加载进来,甚至在编译时期该类的 .class 不存在也可以加载进来。
Class 和 java.lang.reflect 一起对反射提供了支持,java.lang.reflect 类库主要包含了以下三个类:
Field
Method
Constructor
Java反射机制是指在运行时动态地获取一个类的信息并能够操作该类的属性和方法的能力。Java反射机制使得程序能够在运行时借助Class类的API来操作自身的属性和方法,从而大大增强了Java的灵活性和可扩展性。
优缺点
优点:
- 提高了程序的灵活性:可以在运行时获取和操作类的信息,使程序具有更好的灵活性和扩展性。
- 减少了代码的重复性:可以动态地获取和操作类的信息,减少了代码的重复性。
- 提高了程序的可维护性:可以使程序的结构更加清晰明了,提高了程序的可维护性。
缺点:
- 性能较低:Java反射机制是通过运行时动态获取和操作类的信息,性能较低。
- 安全性问题:Java反射机制可以访问和操作类的所有信息,存在安全性问题。
public void test2() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
getAuthor(); //运行时间15
// getAuthorByReflect();//运行时间4378
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行时间:" + (end - start));
}如何获取
//1. 通过类名.class获取
class s = SubjectService.class;
//2.通过Class.forName名获取
class s = Class.forName(SubjectService);
//3.通过对象.getclass获取
class s = data.getClass();
//4.通过类加载器获取
ClassLoader classLoader = Practice0.class.getClassLoader();
Class s = classLoader.loadClass("全类名");比较四种获取方式的区别?通过类加载器获取的方式不常用,在此不做比较。
- 类名.class:JVM将使用类装载器,将类装入内存(前提是:类还没有装入内存),不做类的初始化工作,返回Class的对象。
- Class.forName(“类名字符串”):装入类,并做类的静态初始化,返回Class的对象。
- 实例对象.getClass():对类进行静态初始化、非静态初始化;返回引用运行时真正所指的对象(子对象的引用会赋给父对象的引用变量中)所属的类的Class的对象。
应用场景
- 框架设计:在框架设计中,通常需要使用反射技术来解耦,使框架可扩展和灵活。
- 单元测试:在单元测试中,我们可以使用反射技术来访问私有或受保护的类成员,使测试更加全面。
- 动态代理:使用反射技术可以创建动态代理对象,从而可以在运行时期代理任意一个实现了接口的对象,实现AOP等功能。
- 序列化和反序列化:许多Java序列化和反序列化工具都是基于Java反射机制实现的,例如Java的ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream。
Java反射技术可以在很多场景中应用,尤其是在框架设计和组件化开发中,反射技术可以提高代码的灵活性和可扩展性,减少代码耦合性,简化代码的编写。但是,反射机制也增加了程序的复杂度,因此必须谨慎使用。
执行流程
public class HelloReflect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 1. 使用外部配置的实现,进行动态加载类
TempFunctionTest test = (TempFunctionTest)Class.forName("com.tester.HelloReflect").newInstance();
test.sayHello("call directly");
// 2. 根据配置的函数名,进行方法调用(不需要通用的接口抽象)
Object t2 = new TempFunctionTest();
Method method = t2.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("sayHello", String.class);
method.invoke(test, "method invoke");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void sayHello(String word) {
System.out.println("hello," + word);
}
}
反射获取类实例
获取类信息
首先调用了 java.lang.Class 的静态方法,获取类信息。
@CallerSensitive
public static Class <? > forName(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 先通过反射,获取调用进来的类信息,从而获取当前的 classLoader
Class <? > caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
// 调用native方法进行获取class信息
return forName0(className, true, ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller), caller);
}forName()反射获取类信息,并没有将实现留给了java,而是交给了jvm去加载。
主要是先获取 ClassLoader, 然后调用 native 方法,获取信息,加载类则是回调 java.lang.ClassLoader.
最后,jvm又会回调 ClassLoader 进类加载。
public Class <? > loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
// sun.misc.Launcher
public Class <? > loadClass(String var1, boolean var2) throws ClassNotFoundException {
int var3 = var1.lastIndexOf(46);
if (var3 != -1) {
SecurityManager var4 = System.getSecurityManager();
if (var4 != null) {
var4.checkPackageAccess(var1.substring(0, var3));
}
}
if (this.ucp.knownToNotExist(var1)) {
Class var5 = this.findLoadedClass(var1);
if (var5 != null) {
if (var2) {
this.resolveClass(var5);
}
return var5;
} else {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(var1);
}
} else {
return super.loadClass(var1, var2);
}
}
// java.lang.ClassLoader
protected Class <? > loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 先获取锁
synchronized(getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
// 如果已经加载了的话,就不用再加载了
Class <? > c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
// 双亲委托加载
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
// 父类没有加载到时,再自己加载
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
protected Object getClassLoadingLock(String className) {
Object lock = this;
if (parallelLockMap != null) {
// 使用 ConcurrentHashMap来保存锁
Object newLock = new Object();
lock = parallelLockMap.putIfAbsent(className, newLock);
if (lock == null) {
lock = newLock;
}
}
return lock;
}
protected final Class <? > findLoadedClass(String name) {
if (!checkName(name))
return null;
return findLoadedClass0(name);
}newInstance() 的实现
下面来看一下 newInstance() 的实现方式。
// 首先肯定是 Class.newInstance
@CallerSensitive
public T newInstance() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
//如果存在安全管理器,则调用 checkMemberAccess 方法进行安全检查,以确保调用者具有足够的权限来创建实例。
checkMemberAccess(Member.PUBLIC, Reflection.getCallerClass(), false);
}
// NOTE: the following code may not be strictly correct under
// the current Java memory model.
// Constructor lookup
//如果 cachedConstructor 为空,则查找无参构造函数。
if (cachedConstructor == null) {
if (this == Class.class) {
// 不允许调用 Class 的 newInstance() 方法
throw new IllegalAccessException(
"Can not call newInstance() on the Class for java.lang.Class"
);
}
try {
// 获取无参构造器
Class <? > [] empty = {};
//getConstructor0 方法获取无参构造函数,并将其设置为可访问(setAccessible(true))。
final Constructor < T > c = getConstructor0(empty, Member.DECLARED);
// Disable accessibility checks on the constructor
// since we have to do the security check here anyway
// (the stack depth is wrong for the Constructor's
// security check to work)
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedAction < Void > () {
public Void run() {
c.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
//将获取到的构造函数缓存起来,以便下次调用时可以直接使用。
cachedConstructor = c;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
//如果不存在无参构造函数,那么就会抛出 InstantiationException
throw (InstantiationException) new InstantiationException(getName()).initCause(e);
}
}
//获取缓存的构造函数,并检查其修饰符。
Constructor < T > tmpConstructor = cachedConstructor;
// Security check (same as in java.lang.reflect.Constructor)
int modifiers = tmpConstructor.getModifiers();
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(this, modifiers)) {
//如果快速检查不通过,则获取调用者类,并调用 Reflection.ensureMemberAccess 方法进行更详细的检查,并将调用者类缓存起来。
Class <? > caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (newInstanceCallerCache != caller) {
Reflection.ensureMemberAccess(caller, this, null, modifiers);
newInstanceCallerCache = caller;
}
}
// Run constructor
try {
// 调用无参构造器
return tmpConstructor.newInstance((Object[]) null);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Unsafe.getUnsafe().throwException(e.getTargetException());
// Not reached
return null;
}
}newInstance() 主要做了三件事:
- 权限检测,如果不通过直接抛出异常;
- 查找无参构造器,并将其缓存起来;
- 调用具体方法的无参构造方法,生成实例并返回;
获取构造器
下面是获取构造器的过程:
private Constructor < T > getConstructor0(Class <? > [] parameterTypes, int which) throws NoSuchMethodException {
// 获取所有构造器
Constructor < T > [] constructors = privateGetDeclaredConstructors((which == Member.PUBLIC));
for (Constructor < T > constructor: constructors) {
if (arrayContentsEq(parameterTypes,
constructor.getParameterTypes())) {
return getReflectionFactory().copyConstructor(constructor);
}
}
throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + ".<init>" + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes));
}getConstructor0() 为获取匹配的构造方器;分三步:
- 先获取所有的constructors,然后通过进行参数类型比较;
- 找到匹配后,通过 ReflectionFactory copy一份constructor返回;
- 否则抛出 NoSuchMethodException;
// 获取当前类所有的构造方法,通过jvm或者缓存
// Returns an array of "root" constructors. These Constructor
// objects must NOT be propagated to the outside world, but must
// instead be copied via ReflectionFactory.copyConstructor.
private Constructor < T > [] privateGetDeclaredConstructors(boolean publicOnly) {
checkInitted();
Constructor < T > [] res;
// 调用 reflectionData(), 获取保存的信息,使用软引用保存,从而使内存不够可以回收
ReflectionData < T > rd = reflectionData();
if (rd != null) {
res = publicOnly ? rd.publicConstructors : rd.declaredConstructors;
// 存在缓存,则直接返回
if (res != null) return res;
}
// No cached value available; request value from VM
if (isInterface()) {@
SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Constructor < T > [] temporaryRes = (Constructor < T > []) new Constructor <? > [0];
res = temporaryRes;
} else {
// 使用native方法从jvm获取构造器
res = getDeclaredConstructors0(publicOnly);
}
if (rd != null) {
// 最后,将从jvm中读取的内容,存入缓存
if (publicOnly) {
rd.publicConstructors = res;
} else {
rd.declaredConstructors = res;
}
}
return res;
}
// Lazily create and cache ReflectionData
private ReflectionData < T > reflectionData() {
SoftReference < ReflectionData < T >> reflectionData = this.reflectionData;
int classRedefinedCount = this.classRedefinedCount;
ReflectionData < T > rd;
if (useCaches &&
reflectionData != null &&
(rd = reflectionData.get()) != null &&
rd.redefinedCount == classRedefinedCount) {
return rd;
}
// else no SoftReference or cleared SoftReference or stale ReflectionData
// -> create and replace new instance
return newReflectionData(reflectionData, classRedefinedCount);
}
// 新创建缓存,保存反射信息
private ReflectionData < T > newReflectionData(SoftReference < ReflectionData < T >> oldReflectionData,
int classRedefinedCount) {
if (!useCaches) return null;
// 使用cas保证更新的线程安全性,所以反射是保证线程安全的
while (true) {
ReflectionData < T > rd = new ReflectionData < > (classRedefinedCount);
// try to CAS it...
if (Atomic.casReflectionData(this, oldReflectionData, new SoftReference < > (rd))) {
return rd;
}
// 先使用CAS更新,如果更新成功,则立即返回,否则测查当前已被其他线程更新的情况,如果和自己想要更新的状态一致,则也算是成功了
oldReflectionData = this.reflectionData;
classRedefinedCount = this.classRedefinedCount;
if (oldReflectionData != null &&
(rd = oldReflectionData.get()) != null &&
rd.redefinedCount == classRedefinedCount) {
return rd;
}
}
}如上,privateGetDeclaredConstructors(), 获取所有的构造器主要步骤;
- 先尝试从缓存中获取;
- 如果缓存没有,则从jvm中重新获取,并存入缓存,缓存使用软引用进行保存,保证内存可用;
另外,使用 relactionData() 进行缓存保存;ReflectionData 的数据结构如下。
// reflection data that might get invalidated when JVM TI RedefineClasses() is called
private static class ReflectionData < T > {
volatile Field[] declaredFields;
volatile Field[] publicFields;
volatile Method[] declaredMethods;
volatile Method[] publicMethods;
volatile Constructor < T > [] declaredConstructors;
volatile Constructor < T > [] publicConstructors;
// Intermediate results for getFields and getMethods
volatile Field[] declaredPublicFields;
volatile Method[] declaredPublicMethods;
volatile Class <? > [] interfaces;
// Value of classRedefinedCount when we created this ReflectionData instance
final int redefinedCount;
ReflectionData(int redefinedCount) {
this.redefinedCount = redefinedCount;
}
}其中,还有一个点,就是如何比较构造是否是要查找构造器,其实就是比较类型完成相等就完了,有一个不相等则返回false。
private static boolean arrayContentsEq(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) {
if (a1 == null) {
return a2 == null || a2.length == 0;
}
if (a2 == null) {
return a1.length == 0;
}
if (a1.length != a2.length) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a1.length; i++) {
if (a1[i] != a2[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory
/** Makes a copy of the passed constructor. The returned
constructor is a "child" of the passed one; see the comments
in Constructor.java for details. */
public < T > Constructor < T > copyConstructor(Constructor < T > arg) {
return langReflectAccess().copyConstructor(arg);
}
// java.lang.reflect.Constructor, copy 其实就是新new一个 Constructor 出来
Constructor < T > copy() {
// This routine enables sharing of ConstructorAccessor objects
// among Constructor objects which refer to the same underlying
// method in the VM. (All of this contortion is only necessary
// because of the "accessibility" bit in AccessibleObject,
// which implicitly requires that new java.lang.reflect
// objects be fabricated for each reflective call on Class
// objects.)
if (this.root != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not copy a non-root Constructor");
Constructor < T > res = new Constructor < > (clazz,
parameterTypes,
exceptionTypes, modifiers, slot,
signature,
annotations,
parameterAnnotations);
// root 指向当前 constructor
res.root = this;
// Might as well eagerly propagate this if already present
res.constructorAccessor = constructorAccessor;
return res;
}通过上面,获取到 Constructor 了。
接下来就只需调用其相应构造器的 newInstance(),即返回实例了。
// return tmpConstructor.newInstance((Object[])null);
// java.lang.reflect.Constructor
@CallerSensitive
public T newInstance(Object...initargs) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class <? > caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, null, modifiers);
}
}
if ((clazz.getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects");
ConstructorAccessor ca = constructorAccessor; // read volatile
if (ca == null) {
ca = acquireConstructorAccessor();
}@
SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T inst = (T) ca.newInstance(initargs);
return inst;
}
// sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl
public Object newInstance(Object[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
return delegate.newInstance(args);
}
// sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl
public Object newInstance(Object[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// We can't inflate a constructor belonging to a vm-anonymous class
// because that kind of class can't be referred to by name, hence can't
// be found from the generated bytecode.
if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold() && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(c.getDeclaringClass())) {
ConstructorAccessorImpl acc = (ConstructorAccessorImpl)
new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateConstructor(c.getDeclaringClass(),
c.getParameterTypes(),
c.getExceptionTypes(),
c.getModifiers());
parent.setDelegate(acc);
}
// 调用native方法,进行调用 constructor
return newInstance0(c, args);
}返回构造器的实例后,可以根据外部进行进行类型转换,从而使用接口或方法进行调用实例功能了。
获取类实例两种方式的区别
- Class.newInstance():只能够调用无参的构造函数,即默认的构造函数;并且要求被调用的构造函数是可见的,也即必须是public类型的;
- Constructor.newInstance():可以根据传入的参数,调用任意构造构造函数;可以调用私有的构造函数。
在JDK9之后 class.newInstance()方法就被弃用了,详情可以看这篇文章 弃用class-newinstance
反射获取方法
获取 Method
// java.lang.Class
@CallerSensitive
public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class <? > ...parameterTypes)
throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
checkMemberAccess(Member.DECLARED, Reflection.getCallerClass(), true);
Method method = searchMethods(privateGetDeclaredMethods(false), name, parameterTypes);
if (method == null) {
throw new NoSuchMethodException(getName() + "." + name + argumentTypesToString(parameterTypes));
}
return method;
}忽略第一个检查权限,剩下就只有两个动作了。
获取所有方法列表;
根据方法名称和方法列表,选出符合要求的方法;
如果没有找到相应方法,抛出异常,否则返回对应方法;
所以,先看一下怎样获取类声明的所有方法
// Returns an array of "root" methods. These Method objects must NOT
// be propagated to the outside world, but must instead be copied
// via ReflectionFactory.copyMethod.
private Method[] privateGetDeclaredMethods(boolean publicOnly) {
checkInitted();
Method[] res;
ReflectionData < T > rd = reflectionData();
if (rd != null) {
res = publicOnly ? rd.declaredPublicMethods : rd.declaredMethods;
if (res != null) return res;
}
// No cached value available; request value from VM
res = Reflection.filterMethods(this, getDeclaredMethods0(publicOnly));
if (rd != null) {
if (publicOnly) {
rd.declaredPublicMethods = res;
} else {
rd.declaredMethods = res;
}
}
return res;
}很相似,和获取所有构造器的方法很相似,都是先从缓存中获取方法,如果没有,则从jvm中获取。
不同的是,方法列表需要进行过滤 Reflection.filterMethods;当然后面看来,这个方法我们一般不会派上用场。
// sun.misc.Reflection
public static Method[] filterMethods(Class <? > containingClass, Method[] methods) {
if (methodFilterMap == null) {
// Bootstrapping
return methods;
}
return (Method[]) filter(methods, methodFilterMap.get(containingClass));
}
// 可以过滤指定的方法,一般为空,如果要指定过滤,可以调用 registerMethodsToFilter(), 或者...
private static Member[] filter(Member[] members, String[] filteredNames) {
if ((filteredNames == null) || (members.length == 0)) {
return members;
}
int numNewMembers = 0;
for (Member member: members) {
boolean shouldSkip = false;
for (String filteredName: filteredNames) {
if (member.getName() == filteredName) {
shouldSkip = true;
break;
}
}
if (!shouldSkip) {
++numNewMembers;
}
}
Member[] newMembers =
(Member[]) Array.newInstance(members[0].getClass(), numNewMembers);
int destIdx = 0;
for (Member member: members) {
boolean shouldSkip = false;
for (String filteredName: filteredNames) {
if (member.getName() == filteredName) {
shouldSkip = true;
break;
}
}
if (!shouldSkip) {
newMembers[destIdx++] = member;
}
}
return newMembers;
}根据方法名和参数类型过滤指定方法返回
private static Method searchMethods(Method[] methods, String name, Class <? > [] parameterTypes) {
Method res = null;
// 使用常量池,避免重复创建String
String internedName = name.intern();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
Method m = methods[i];
if (m.getName() == internedName && arrayContentsEq(parameterTypes, m.getParameterTypes())
&& (res == null || res.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(m.getReturnType())))
res = m;
}
return (res == null ? res : getReflectionFactory().copyMethod(res));
}大概意思看得明白,就是匹配到方法名,然后参数类型匹配,才可以。
但是可以看到,匹配到一个方法,并没有退出for循环,而是继续进行匹配。
这里是匹配最精确的子类进行返回(最优匹配)
最后,还是通过 ReflectionFactory, copy 方法后返回。
调用 method.invoke() 方法
@CallerSensitive
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object...args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class <? > caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}invoke时,是通过 MethodAccessor 进行调用的,而 MethodAccessor 是个接口,在第一次时调用 acquireMethodAccessor() 进行新创建。
// probably make the implementation more scalable.
private MethodAccessor acquireMethodAccessor() {
// First check to see if one has been created yet, and take it
// if so
MethodAccessor tmp = null;
if (root != null) tmp = root.getMethodAccessor();
if (tmp != null) {
// 存在缓存时,存入 methodAccessor,否则调用 ReflectionFactory 创建新的 MethodAccessor
methodAccessor = tmp;
} else {
// Otherwise fabricate one and propagate it up to the root
tmp = reflectionFactory.newMethodAccessor(this);
setMethodAccessor(tmp);
}
return tmp;
}
// sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory
public MethodAccessor newMethodAccessor(Method method) {
checkInitted();
if (noInflation && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
} else {
NativeMethodAccessorImpl acc =
new NativeMethodAccessorImpl(method);
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl res =
new DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(acc);
acc.setParent(res);
return res;
}
}两个Accessor详情:
//NativeMethodAccessorImpl / DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl
class NativeMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
private final Method method;
private DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl parent;
private int numInvocations;
NativeMethodAccessorImpl(Method method) {
this.method = method;
}
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
// We can't inflate methods belonging to vm-anonymous classes because
// that kind of class can't be referred to by name, hence can't be
// found from the generated bytecode.
if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold()
&& !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
MethodAccessorImpl acc = (MethodAccessorImpl)
new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
parent.setDelegate(acc);
}
return invoke0(method, obj, args);
}
void setParent(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
private static native Object invoke0(Method m, Object obj, Object[] args);
}
class DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
private MethodAccessorImpl delegate;
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {
setDelegate(delegate);
}
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
return delegate.invoke(obj, args);
}
void setDelegate(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
}进行 ma.invoke(obj, args); 调用时,调用 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke();
最后被委托到 NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(), 即:
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// We can't inflate methods belonging to vm-anonymous classes because
// that kind of class can't be referred to by name, hence can't be
// found from the generated bytecode.
if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold() && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
MethodAccessorImpl acc = (MethodAccessorImpl)
new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
parent.setDelegate(acc);
}
// invoke0 是个 native 方法,由jvm进行调用业务方法。从而完成反射调用功能。
return invoke0(method, obj, args);
}其中, generateMethod() 是生成具体类的方法:
/** This routine is not thread-safe */
public MethodAccessor generateMethod(Class <? > declaringClass,
String name,
Class <? > [] parameterTypes,
Class <? > returnType,
Class <? > [] checkedExceptions,
int modifiers) {
return (MethodAccessor) generate(declaringClass,
name,
parameterTypes,
returnType,
checkedExceptions,
modifiers,
false,
false,
null);
}generate() 戳详情。
/** This routine is not thread-safe */
private MagicAccessorImpl generate(final Class <? > declaringClass,
String name,
Class <? > [] parameterTypes,
Class <? > returnType,
Class <? > [] checkedExceptions,
int modifiers,
boolean isConstructor,
boolean forSerialization,
Class <? > serializationTargetClass) {
ByteVector vec = ByteVectorFactory.create();
asm = new ClassFileAssembler(vec);
this.declaringClass = declaringClass;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.returnType = returnType;
this.modifiers = modifiers;
this.isConstructor = isConstructor;
this.forSerialization = forSerialization;
asm.emitMagicAndVersion();
// Constant pool entries:
// ( * = Boxing information: optional)
// (+ = Shared entries provided by AccessorGenerator)
// (^ = Only present if generating SerializationConstructorAccessor)
// [UTF-8] [This class's name]
// [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// [UTF-8] "sun/reflect/{MethodAccessorImpl,ConstructorAccessorImpl,SerializationConstructorAccessorImpl}"
// [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// [UTF-8] [Target class's name]
// [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// ^ [UTF-8] [Serialization: Class's name in which to invoke constructor]
// ^ [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// [UTF-8] target method or constructor name
// [UTF-8] target method or constructor signature
// [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// [CONSTANT_Methodref_info or CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info] for target method
// [UTF-8] "invoke" or "newInstance"
// [UTF-8] invoke or newInstance descriptor
// [UTF-8] descriptor for type of non-primitive parameter 1
// [CONSTANT_Class_info] for type of non-primitive parameter 1
// ...
// [UTF-8] descriptor for type of non-primitive parameter n
// [CONSTANT_Class_info] for type of non-primitive parameter n
// + [UTF-8] "java/lang/Exception"
// + [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// + [UTF-8] "java/lang/ClassCastException"
// + [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// + [UTF-8] "java/lang/NullPointerException"
// + [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// + [UTF-8] "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException"
// + [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// + [UTF-8] "java/lang/InvocationTargetException"
// + [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// + [UTF-8] "<init>"
// + [UTF-8] "()V"
// + [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// + [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for NullPointerException's constructor
// + [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for IllegalArgumentException's constructor
// + [UTF-8] "(Ljava/lang/String;)V"
// + [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for "<init>(Ljava/lang/String;)V"
// + [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for IllegalArgumentException's constructor taking a String
// + [UTF-8] "(Ljava/lang/Throwable;)V"
// + [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for "<init>(Ljava/lang/Throwable;)V"
// + [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for InvocationTargetException's constructor
// + [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for "super()"
// + [UTF-8] "java/lang/Object"
// + [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// + [UTF-8] "toString"
// + [UTF-8] "()Ljava/lang/String;"
// + [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for "toString()Ljava/lang/String;"
// + [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for Object's toString method
// + [UTF-8] "Code"
// + [UTF-8] "Exceptions"
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Boolean"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(Z)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "booleanValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()Z"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Byte"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(B)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "byteValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()B"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Character"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(C)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "charValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()C"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Double"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(D)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "doubleValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()D"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Float"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(F)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "floatValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()F"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Integer"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(I)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "intValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()I"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Long"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(J)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "longValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()J"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "java/lang/Short"
// * [CONSTANT_Class_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "(S)V"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
// * [UTF-8] "shortValue"
// * [UTF-8] "()S"
// * [CONSTANT_NameAndType_info] for above
// * [CONSTANT_Methodref_info] for above
short numCPEntries = NUM_BASE_CPOOL_ENTRIES + NUM_COMMON_CPOOL_ENTRIES;
boolean usesPrimitives = usesPrimitiveTypes();
if (usesPrimitives) {
numCPEntries += NUM_BOXING_CPOOL_ENTRIES;
}
if (forSerialization) {
numCPEntries += NUM_SERIALIZATION_CPOOL_ENTRIES;
}
// Add in variable-length number of entries to be able to describe
// non-primitive parameter types and checked exceptions.
numCPEntries += (short)(2 * numNonPrimitiveParameterTypes());
asm.emitShort(add(numCPEntries, S1));
final String generatedName = generateName(isConstructor, forSerialization);
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8(generatedName);
asm.emitConstantPoolClass(asm.cpi());
thisClass = asm.cpi();
if (isConstructor) {
if (forSerialization) {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8("sun/reflect/SerializationConstructorAccessorImpl");
} else {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8("sun/reflect/ConstructorAccessorImpl");
}
} else {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8("sun/reflect/MethodAccessorImpl");
}
asm.emitConstantPoolClass(asm.cpi());
superClass = asm.cpi();
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8(getClassName(declaringClass, false));
asm.emitConstantPoolClass(asm.cpi());
targetClass = asm.cpi();
short serializationTargetClassIdx = (short) 0;
if (forSerialization) {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8(getClassName(serializationTargetClass, false));
asm.emitConstantPoolClass(asm.cpi());
serializationTargetClassIdx = asm.cpi();
}
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8(name);
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8(buildInternalSignature());
asm.emitConstantPoolNameAndType(sub(asm.cpi(), S1), asm.cpi());
if (isInterface()) {
asm.emitConstantPoolInterfaceMethodref(targetClass, asm.cpi());
} else {
if (forSerialization) {
asm.emitConstantPoolMethodref(serializationTargetClassIdx, asm.cpi());
} else {
asm.emitConstantPoolMethodref(targetClass, asm.cpi());
}
}
targetMethodRef = asm.cpi();
if (isConstructor) {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8("newInstance");
} else {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8("invoke");
}
invokeIdx = asm.cpi();
if (isConstructor) {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8("([Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;");
} else {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8("(Ljava/lang/Object;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;");
}
invokeDescriptorIdx = asm.cpi();
// Output class information for non-primitive parameter types
nonPrimitiveParametersBaseIdx = add(asm.cpi(), S2);
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
Class <? > c = parameterTypes[i];
if (!isPrimitive(c)) {
asm.emitConstantPoolUTF8(getClassName(c, false));
asm.emitConstantPoolClass(asm.cpi());
}
}
// Entries common to FieldAccessor, MethodAccessor and ConstructorAccessor
emitCommonConstantPoolEntries();
// Boxing entries
if (usesPrimitives) {
emitBoxingContantPoolEntries();
}
if (asm.cpi() != numCPEntries) {
throw new InternalError("Adjust this code (cpi = " + asm.cpi() +
", numCPEntries = " + numCPEntries + ")");
}
// Access flags
asm.emitShort(ACC_PUBLIC);
// This class
asm.emitShort(thisClass);
// Superclass
asm.emitShort(superClass);
// Interfaces count and interfaces
asm.emitShort(S0);
// Fields count and fields
asm.emitShort(S0);
// Methods count and methods
asm.emitShort(NUM_METHODS);
emitConstructor();
emitInvoke();
// Additional attributes (none)
asm.emitShort(S0);
// Load class
vec.trim();
final byte[] bytes = vec.getData();
// Note: the class loader is the only thing that really matters
// here -- it's important to get the generated code into the
// same namespace as the target class. Since the generated code
// is privileged anyway, the protection domain probably doesn't
// matter.
return AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction < MagicAccessorImpl > () {
public MagicAccessorImpl run() {
try {
return (MagicAccessorImpl)
ClassDefiner.defineClass(generatedName,
bytes,
0,
bytes.length,
declaringClass.getClassLoader()).newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
});
}主要看这一句:ClassDefiner.defineClass(xx, declaringClass.getClassLoader()).newInstance();
在ClassDefiner.defineClass方法实现中,每被调用一次都会生成一个DelegatingClassLoader类加载器对象 ,这里每次都生成新的类加载器,是为了性能考虑,在某些情况下可以卸载这些生成的类,因为类的卸载是只有在类加载器可以被回收的情况下才会被回收的,如果用了原来的类加载器,那可能导致这些新创建的类一直无法被卸载。
而反射生成的类,有时候可能用了就可以卸载了,所以使用其独立的类加载器,从而使得更容易控制反射类的生命周期。
反射调用流程小结
- 反射类及反射方法的获取,都是通过从列表中搜寻查找匹配的方法,所以查找性能会随类的大小方法多少而变化;
- 每个类都会有一个与之对应的Class实例,从而每个类都可以获取method反射方法,并作用到其他实例身上;
- 反射也是考虑了线程安全的,放心使用;
- 反射使用软引用relectionData缓存class信息,避免每次重新从jvm获取带来的开销;
- 反射调用多次生成新代理Accessor, 而通过字节码生存的则考虑了卸载功能,所以会使用独立的类加载器;
- 当找到需要的方法,都会copy一份出来,而不是使用原来的实例,从而保证数据隔离;
- 调度反射方法,最终是由jvm执行invoke0()执行;
反射为什么慢
为了放大问题,找到共性,采用逐渐扩大测试次数、每次测试多次取平均值的方式,针对同一个方法分别就直接调用该方法、反射调用该方法、直接调用该方法对应的实例、反射调用该方法对应的实例分别从 1-1000000,每隔一个数量级测试一次:
测试代码如下:
public class ReflectionPerformanceActivity extends Activity{
private TextView mExecuteResultTxtView = null;
private EditText mExecuteCountEditTxt = null;
private Executor mPerformanceExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
private static final int AVERAGE_COUNT = 10;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_reflection_performance_layout);
mExecuteResultTxtView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.executeResultTxtId);
mExecuteCountEditTxt = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.executeCountEditTxtId);
}
public void onClick(View v){
switch(v.getId()){
case R.id.executeBtnId:{
execute();
}
break;
default:{
}
break;
}
}
private void execute(){
mExecuteResultTxtView.setText("");
mPerformanceExecutor.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
long costTime = 0;
int executeCount = Integer.parseInt(mExecuteCountEditTxt.getText().toString());
long reflectMethodCostTime=0,normalMethodCostTime=0,reflectFieldCostTime=0,normalFieldCostTime=0;
updateResultTextView(executeCount + "毫秒耗时情况测试");
for(int index = 0; index < AVERAGE_COUNT; index++){
updateResultTextView("第 " + (index+1) + " 次");
costTime = getNormalCallCostTime(executeCount);
reflectMethodCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行直接调用方法耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
costTime = getReflectCallMethodCostTime(executeCount);
normalMethodCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用方法耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
costTime = getNormalFieldCostTime(executeCount);
reflectFieldCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行普通调用实例耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
costTime = getReflectCallFieldCostTime(executeCount);
normalFieldCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用实例耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
}
updateResultTextView("执行直接调用方法平均耗时:" + reflectMethodCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用方法平均耗时:" + normalMethodCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
updateResultTextView("执行普通调用实例平均耗时:" + reflectFieldCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用实例平均耗时:" + normalFieldCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
}
});
}
private long getReflectCallMethodCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
try{
Method setmLanguageMethod = programMonkey.getClass().getMethod("setmLanguage", String.class);
setmLanguageMethod.setAccessible(true);
setmLanguageMethod.invoke(programMonkey, "Java");
}catch(IllegalAccessException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(InvocationTargetException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(NoSuchMethodException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getReflectCallFieldCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
try{
Field ageField = programMonkey.getClass().getDeclaredField("mLanguage");
ageField.set(programMonkey, "Java");
}catch(NoSuchFieldException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IllegalAccessException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getNormalCallCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
programMonkey.setmLanguage("Java");
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getNormalFieldCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
programMonkey.mLanguage = "Java";
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private void updateResultTextView(final String content){
ReflectionPerformanceActivity.this.runOnUiThread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
mExecuteResultTxtView.append(content);
mExecuteResultTxtView.append("\n");
}
});
}
}测试结果如下:

测试结论:
反射的确会导致性能问题。反射导致的性能问题是否严重跟使用的次数有关系,如果控制在100次以内,基本上没什么差别,如果调用次数超过了100次,性能差异会很明显。
四种访问方式,直接访问实例的方式效率最高;其次是直接调用方法的方式,耗时约为直接调用实例的 1.4 倍;接着是通过反射访问实例的方式,耗时约为直接访问实例的 3.75 倍;最慢的是通过反射访问方法的方式,耗时约为直接访问实例的 6.2 倍。
到底慢在哪?
跟踪源码可以发现,四个方法中都存在实例化ProgramMonkey的代码,所以可以排除是这句话导致的不同调用方式产生的性能差异;通过反射调用方法中调用了setAccessible方法,但该方法纯粹只是设置属性值,不会产生明显的性能差异;所以最有可能产生性能差异的只有getMethod和getDeclaredField、invoke和set方法了,下面分别就这两组方法进行测试,找到具体慢在哪?
首先测试invoke和set方法,修改getReflectCallMethodCostTime和getReflectCallFieldCostTime方法的代码如下:
private long getReflectCallMethodCostTime(int count) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
Method setmLanguageMethod = null;
try {
setmLanguageMethod = programMonkey.getClass().getMethod("setmLanguage", String.class);
setmLanguageMethod.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int index = 0; index < count; index++) {
try {
setmLanguageMethod.invoke(programMonkey, "Java");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
}
private long getReflectCallFieldCostTime(int count) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
Field ageField = null;
try {
ageField = programMonkey.getClass().getDeclaredField("mLanguage");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int index = 0; index < count; index++) {
try {
ageField.set(programMonkey, "Java");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
}沿用上面的测试方法,测试结果如下:
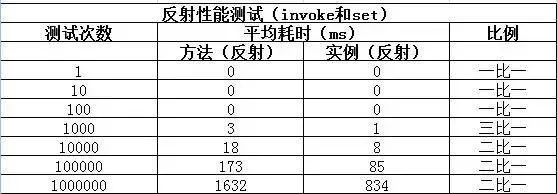
修改getReflectCallMethodCostTime和getReflectCallFieldCostTime方法的代码如下,对getMethod和getDeclaredField进行测试:
private long getReflectCallMethodCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
try{
Method setmLanguageMethod = programMonkey.getClass().getMethod("setmLanguage", String.class);
}catch(NoSuchMethodException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getReflectCallFieldCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
try{
Field ageField = programMonkey.getClass().getDeclaredField("mLanguage");
}catch(NoSuchFieldException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}沿用上面的测试方法,测试结果如下:
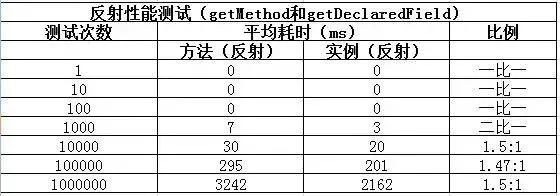
测试结论:
getMethod和getDeclaredField方法会比invoke和set方法耗时;- 随着测试数量级越大,性能差异的比例越趋于稳定;
由于测试的这四个方法最终调用的都是native方法,无法进一步跟踪。个人猜测应该是和在程序运行时操作class有关。
比如需要判断是否安全?是否允许这样操作?入参是否正确?是否能够在虚拟机中找到需要反射的类?主要是这一系列判断条件导致了反射耗时;也有可能是因为调用natvie方法,需要使用JNI接口,导致了性能问题(参照Log.java、System.out.println,都是调用native方法,重复调用多次耗时很明显)。
如何避免反射导致的性能问题?
通过上面的测试可以看出,过多地使用反射,的确会存在性能问题,但如果使用得当,所谓反射导致性能问题也就不是问题了,关于反射对性能的影响,参照下面的使用原则,并不会有什么明显的问题:
- 不要过于频繁地使用反射,大量地使用反射会带来性能问题;
- 通过反射直接访问实例会比访问方法快很多,所以应该优先采用访问实例的方式。
小结
上面的测试并不全面,但在一定程度上能够反映出反射的确会导致性能问题,也能够大概知道是哪个地方导致的问题。如果后面有必要进一步测试,可以从下面几个方面作进一步测试:
- 测试频繁调用
native方法是否会有明显的性能问题; - 测试同一个方法内,过多的条件判断是否会有明显的性能问题;
- 测试类的复杂程度是否会对反射的性能有明显影响。